MTT has multiple advantages, providing professional and highly compatible HBM and LU testing services, with flexible configuration and advanced monitoring functions, to assist product quality and provide professional and reliable testing support.

| Project Overview
1. Human Body Model Electrostatic Discharge (HBM ESD) is the earliest established and most widely used simulated electrostatic testing model. HBM is the abbreviation for Human Body Model, which represents the human electrostatic discharge model. When a person accumulates static electricity on the body through walking on the ground, friction, or other factors, and then touches an IC, the static electricity from the human body is discharged into the contacted device. The HBM ESD model simulates situations in which a charged human body comes into contact with or approaches electrostatic discharge sensitive devices (ESDS), where the components may be damaged either by direct electrostatic discharge or by electrostatic fields.
2. Latch-up: Triggered by parasitic structures within an IC, causing the formation of a low-impedance path inside the chip, which leads to the persistence of high current. Even after the triggering conditions are removed, the high current continues to flow. Only by powering off can the device exit the latch-up (LU) state. Causes of latch-up triggering: excessive voltage, improper power management sequencing, electrostatic discharge (ESD), and similar factors.
| Test Objective
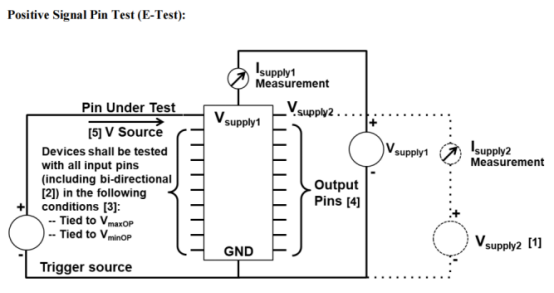
1. Simulate the discharge condition when a charged human body touches the device, to evaluate the device’s tolerance to electrostatic discharge (ESD).
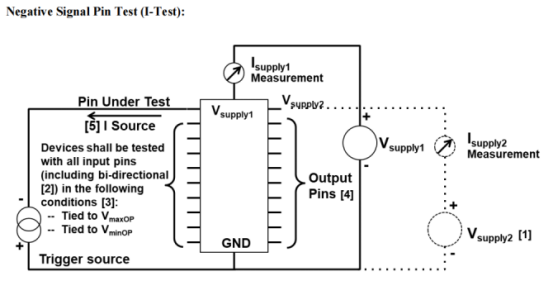
2. Assess the device’s resistance to latch-up effects, preventing the formation of low-impedance paths within the device caused by overvoltage or overcurrent, which could otherwise result in damage or failure.
| Test Standard
1.ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001-2024 Human Body Model (HBM) Device Level、MIL-STD-883E、AEC Q100-002E;
2.JEDEC JESD78F.02-2023 IC Latch-Up Test - Minor Revision of JESD78F.01, December 2022.
| Service Products / Fields
1. HBM: Widely applied in automotive electronics, consumer electronics, industrial electronics, and other fields.
2. LU: High-reliability fields such as automotive electronics and aerospace.
| Project Advantages
1. Compatibility with multiple testing methods and standards.
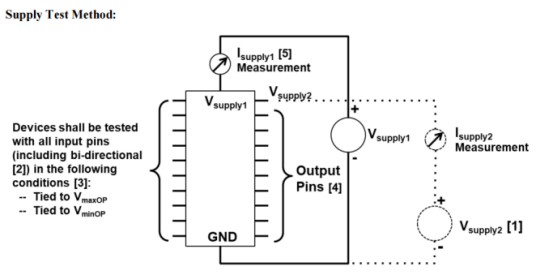
2. Highly flexible biasing and pin configuration capabilities.
3. Advanced control and monitoring functions.
4. Leakage current or DC IV characteristic scanning.
| Test Principle Diagram
HBM
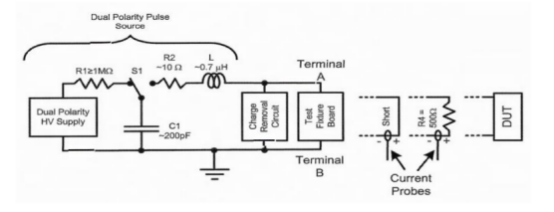
LU