




























Reliability testing refers to activities carried out to evaluate whether a product can maintain its functional reliability throughout its specified service life, under all anticipated environments such as use, transportation, or storage.
| What is a reliability test?
Reliability refers to the ability of a product to perform its specified functions under specified conditions within a specified period of time. The product here can generally refer to any system, equipment, and component.
The elements of the product reliability definition are three "specifications": "specified conditions", "specified time", and "specified functions".
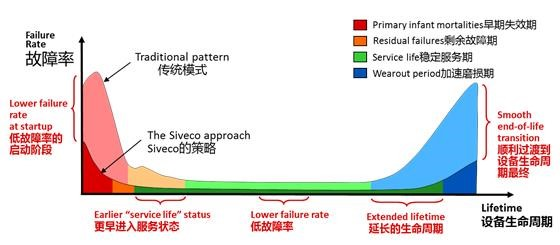
Products with higher reliability have a longer lifespan and better performance.
Generally speaking, products with higher reliability have higher R&D and production costs, but lower post-maintenance costs;
Generally speaking, products with lower reliability have lower R&D and production costs, but higher post-maintenance costs.
Therefore, there is theoretically a curve of product reliability versus product life-cycle cost, and when the reliability reaches a certain value, the product life-cycle cost is minimized.
| Project Overview
Reliability testing refers to activities carried out to evaluate whether a product can maintain its functional reliability throughout its specified service life, under all anticipated environments such as use, transportation, or storage. It involves subjecting the product to natural or artificially created environmental conditions in order to assess its performance under actual usage, transport, and storage environments, while also analyzing the extent and mechanisms of environmental influences.
| Test Objective
1. In the development phase, it is used to expose defects in various aspects of the trial-produced product and evaluate whether the product reliability meets the predetermined indicators;
2. In the production stage, it provides information for monitoring the production process;
3. Conduct reliability appraisal or acceptance for finalized products;
4. Expose and analyze the failure laws, relevant failure modes and failure mechanisms of products under different environmental and stress conditions;
5. Provide a basis for improving product reliability, formulating and improving reliability test plans, and for users to select products.
| Test Method
For different products, different reliability test methods can be selected to achieve different purposes.
MTT specializes in providing reliability testing services, which are mainly classified into three parts: electrical performance testing, component environmental testing, and component mechanical reliability testing.
Electrical performance testing includes: breakdown voltage, dielectric strength, volume resistivity, surface resistivity, voltage resistance, temperature rise, insulation resistance, etc.
Component environmental testing includes: high/low temperature test, alternating damp-heat test, constant temperature and humidity test, thermal shock test, low-pressure test, ozone test, dust and water resistance test/IP rating, UV ultraviolet aging test, gas corrosion test, salt spray test, etc.
Component mechanical reliability testing includes: vibration test, shock and impact test, collision test, drop test, HALT/HASS test, three-comprehensive test, insertion and extraction force test, etc.