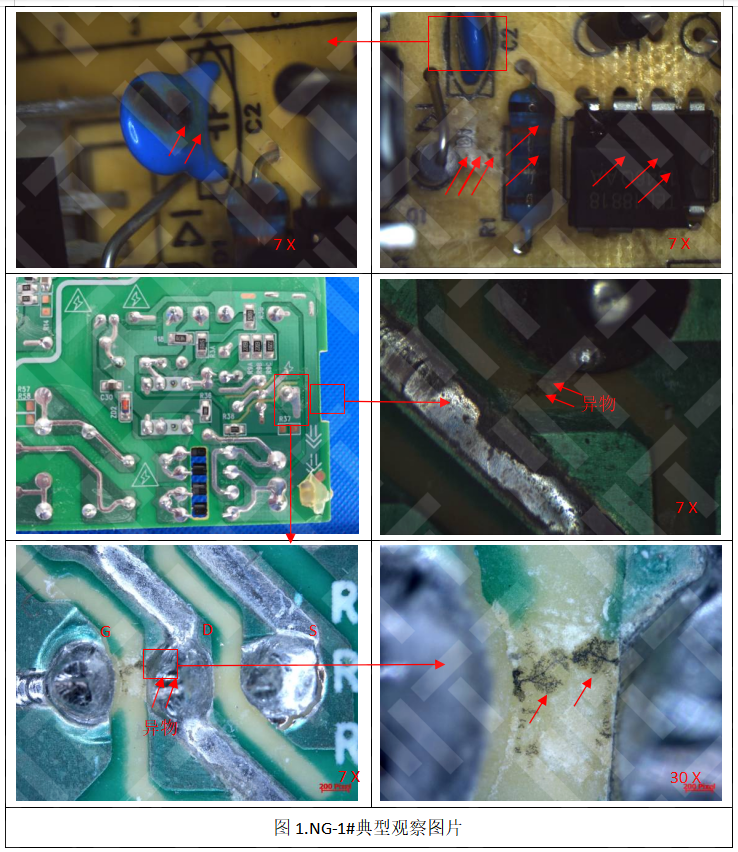
By conducting failure analysis of PCB and PCBA failure phenomena, and through a series of analytical validations, the root causes and mechanisms of failures can be identified. This is of great importance for bettering product quality, improving production processes, and arbitrating failure-related disputes.
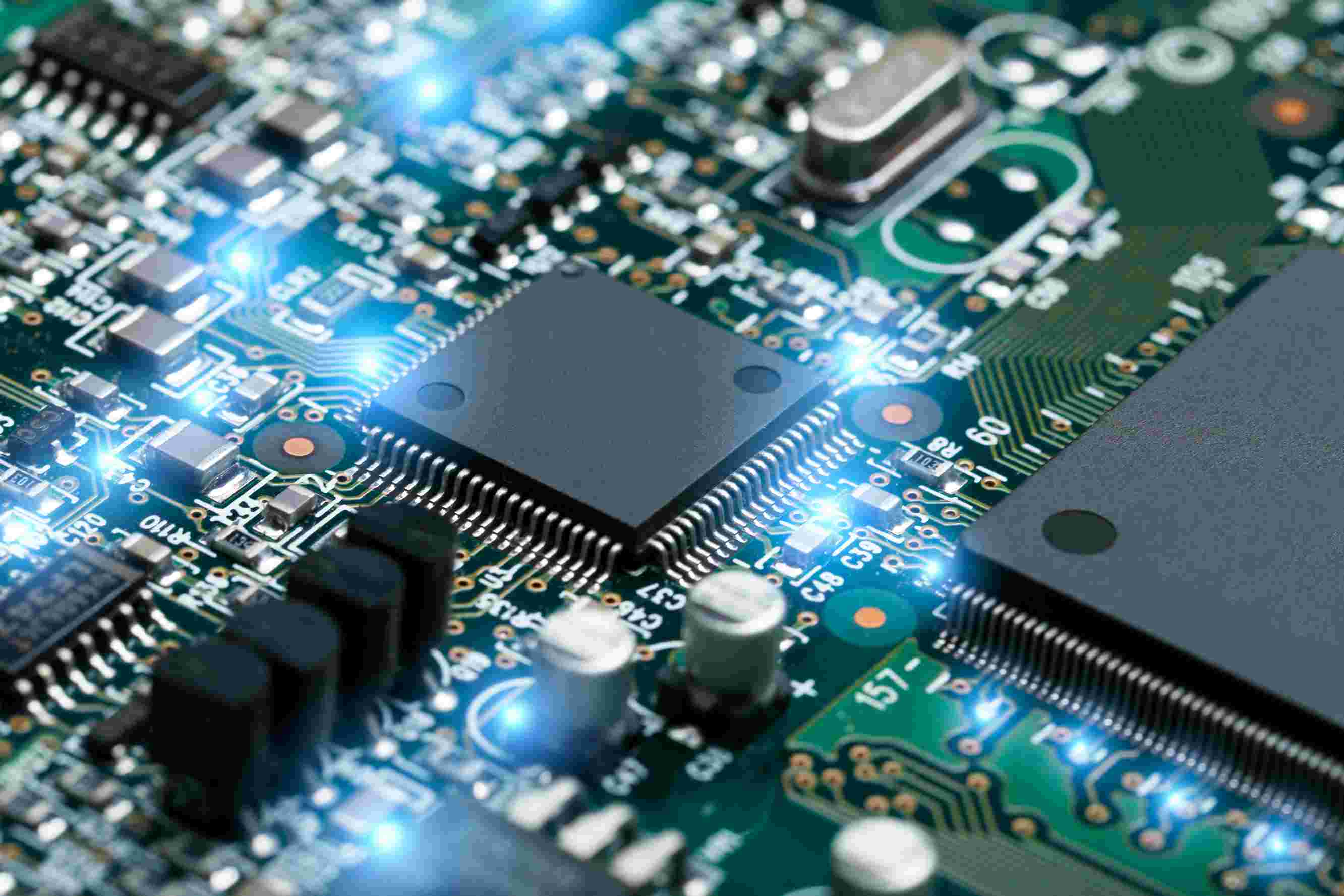
With the increasing density of electronic products and the adoption of lead-free manufacturing, the technical standards and quality requirements of PCB and PCBA products face severe challenges. This necessitates stricter control of processes and raw materials throughout PCB design, production, processing, and assembly. At present, since the industry is still in a phase of technological and process transformation, customers have varying levels of understanding of PCB fabrication and assembly processes. As a result, failures such as leakage, open circuits (in traces or vias), poor soldering, and board delamination frequently occur, often causing quality liability disputes between suppliers and users, which in turn lead to significant economic losses. By conducting failure analysis of PCB and PCBA failure phenomena, and through a series of analytical validations, the root causes and mechanisms of failures can be identified. This is of great importance for bettering product quality, improving production processes, and arbitrating failure-related disputes.
1. Printed Circuit Board and Assembly (PCB & PCBA) Manufacturers: Confirm the quality status of products, analyze various issues arising in the production process, investigate the underlying mechanisms of problems, and provide reference opinions for improving product design and manufacturing processes.
2. Printed Circuit Board and Assembly (PCB & PCBA) Suppliers/Distributors: Control the quality of incoming goods, enhance user confidence in product usage, and strengthen brand value.
3. Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) System Integrators: Eliminate potential issues in the production process in a timely manner, improve the reliability of manufactured products, and reduce liability risks.
Types of PCB/PCBA Analyzed:
Rigid printed circuit boards, flexible printed circuit boards, rigid-flex boards, metal-based boards, ceramic-based boards.
Communication PCBA, lighting PCBA, consumer electronics PCBA, new energy vehicle PCBA, medical equipment PCBA, household appliance PCBA, etc.
1. Assist manufacturers in understanding product quality status, analyzing and evaluating current processes, and optimizing product development plans and manufacturing processes.
2. Identify the root causes of failures in electronic assembly, provide effective on-site process improvement solutions for electronic assembly, and reduce production costs.
3. Improve product yield and operational reliability, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance corporate brand competitiveness.
4. Identify the party responsible for product failures, providing the basis for judicial arbitration.