




























Surface roughness is closely related to the fit properties, wear resistance, fatigue strength, contact stiffness, vibration and noise of mechanical parts, and has an important impact on the service life and reliability of mechanical products.
| Project Overview
Surface roughness refers to the microscopic geometric shape error composed of small spacing and peaks and valleys on the machined surface. The smaller the surface roughness, the smoother the surface. Surface roughness is generally caused by factors such as the friction between the tool and the part surface during the machining process, the plastic deformation of the surface layer metal when the chips are separated, and the high-frequency vibration in the process system. Due to the differences in machining methods and workpiece materials, there are differences in the depth, density, shape and texture of the traces left on the machined surface. Surface roughness is closely related to the fit properties, wear resistance, fatigue strength, contact stiffness, vibration and noise of mechanical parts, and has an important impact on the service life and reliability of mechanical products.
| Test Objective
Surface roughness has an important impact on the service performance of parts, the service life and reliability of products. When designing parts, the corresponding process parameters should be improved according to the surface roughness value of the material and the function of the parts in the machine.
| Testing Standards
JIS B 0601-2013 Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS) Surface texture - Profile method - Terms, definitions and surface texture parameters
| Service Products / Fields
The measurement of surface roughness is mainly applied in fields such as aviation, automobiles, materials, and metal products. Surface roughness has a great impact on the service performance of parts. Generally speaking, a small surface roughness value can improve the quality of the fit, reduce wear and extend the service life of parts. The rougher the surface is, the larger the friction coefficient of the part surface will be, and the faster the wear of the surfaces of two relatively moving parts will be; if the surface is too smooth, the scratching effect of the worn-off metal particles, the extrusion of the lubricating oil, the intermolecular adsorption effect, etc., will also accelerate the wear. For the surfaces of parts with fit requirements, the roughness will affect the stability of the fit properties.
Scope of Application:
Surfaces that have undergone rough machining of semi-finished products and non-mating machined surfaces, such as shaft end faces, chamfers, drilled holes, the sides of gears and pulleys, the bottom surfaces of keyways, and the contact surfaces of washers. Finely machined surfaces, the surfaces of boxes, supports, covers, and sleeves. The taper holes of precision machine tool spindles, the crankshafts of engines, and the tooth surfaces of high-precision gears. The working surfaces of high-precision measuring instruments and gauge blocks, the metal mirrors in optical instruments, etc.
| Typical Images
|
|
|
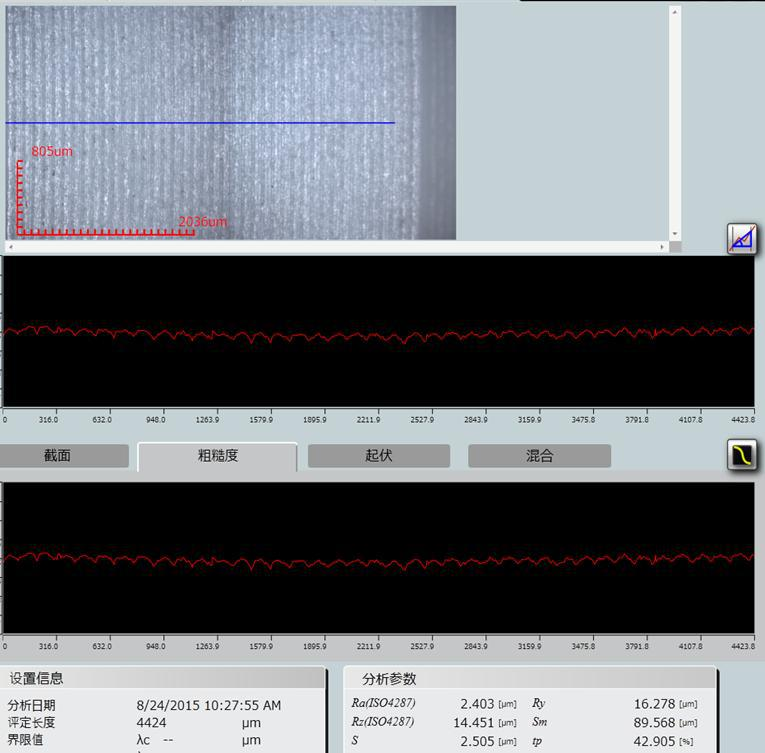
Line roughness |
|
|
|
Surface roughness |
|
|
|
Height measurement |
| MTT Advantages
1. Professional Team: A team of highly experienced testing engineers and technical experts.
2. Advanced Equipment: Equipped with internationally leading testing instruments to ensure accuracy and reliability of results.
3. Efficient Service: Rapidly respond to customer needs and provide one-stop, high-efficiency inspection services.
4. Authoritative Certification: The laboratory is certified by ISO/IEC 17025, ensuring that test reports have international credibility.
Testing Procedure:
Put in the sample → Select the position of the sample to be measured → Set the measurement parameters → Evaluate the measured data → Output the result