




























It can detect in advance the failure risks caused by short-circuits or electrical leakage between metal conductors, ensuring the electrical safety of products. At the same time, it evaluates the cleanliness of PCBs and the reliability of auxiliary materials, preventing early failures caused by contamination or material defects, which is of crucial significance for improving the quality and long-term stability of electronic products.
| Project Background
ECM (Electrochemical Migration) and CAF (Conductive Anodic Filament) are common failure modes in printed circuit boards (PCBs), which may lead to circuit short-circuits, performance degradation, and even equipment malfunctions. With the miniaturization and high-performance development of electronic products, the density and complexity of PCBs are constantly increasing, and the ECM/CAF problems are becoming increasingly prominent. To ensure the reliability and safety of PCB products, ECM/CAF testing has become an indispensable testing step in fields such as electronic manufacturing, automotive electronics, and aerospace.
| Definitions and Hazards of ECM/CAF
Definition of ECM:
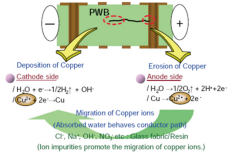
ECM, or Electrochemical Migration, refers to the growth phenomenon of conductive metal filaments on printed wiring boards (PWBs) under DC voltage, which may occur on the outer surface, interface, or structure of the material, and is usually dominated by the migration of ions such as Cu, Ag, and Sn.
Definition of CAF:
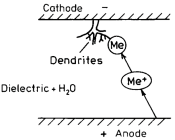
CAF, or Conductive Anodic Filament, is a form of ECM, specifically referring to the conductive filament phenomenon that occurs inside the PCB, and the migrating ions are mainly Cu ions.
Hazards:
ECM/CAF can cause short-circuits in PCB circuits, functional failures, and even pose safety hazards such as fires. In critical fields such as automotive and aerospace, ECM/CAF problems may lead to serious consequences.
| Test Objective
1. Improve the circuit board design or layout;
2. Improve the cleaning materials or processes;
3. Change the flux and/or solder paste;
4. Use new conformal coatings or processes;
5. Evaluate the qualifications of bare board suppliers;
6. Product calibration based on reliability;
7. Change the reflow soldering or wave soldering process.
| Test Principle and Formation Conditions
Test Principle:
The ECM/CAF test simulates a humid environment and applies a DC voltage to prompt the metal ions in the PCB to migrate under the action of an electric field and form conductive filaments.
Formation Conditions:
The formation of ECM/CAF requires conditions such as a humid environment, ion residues, an electric field, and migration channels. Among them, the humid environment is an essential medium for corrosion, ion residues accelerate the speed of corrosion and migration, the electric field provides the driving force for migration, and the migration channels allow ion migration.
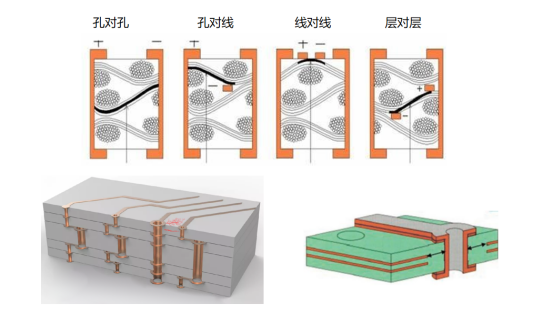
| Service Products / Fields
Service Objects:
It includes materials and products such as solder paste, flux, cleaning agent, three-proof paint, and PCB.
| MTT Advantages
Provide comprehensive ECM/CAF testing services, including testing methods, equipment, processes, etc.
Have a professional technical team and rich testing experience, and can provide customers with accurate test results and solutions.
The test results are scientific and authoritative, and can provide strong support for customers' product improvement and optimization.