Aluminum substrate as a metal-based copper plate with excellent heat dissipation performance, it is widely used in LED lighting products. Its typical structure consists of three layers: circuit layer (copper foil), insulation layer and metal base. Improving the reliability of aluminum substrates can ensure product quality, reduce costs, and enhance brand image, which is of great significance to the development of the electronics industry and user safety.
However, recently in the production process, it was found that although a batch of aluminum substrates was not abnormal after three reflows, there was a local drum kit phenomenon in the repair stage. This article will elaborate on the analysis of this problem and propose corresponding improvement measures.
1. Appearance analysis
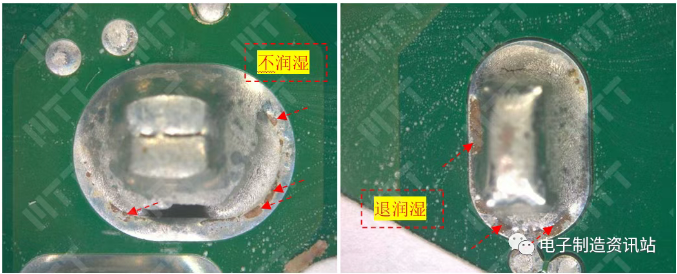
NG sample found in multiple locations of drum kit anomalies, drum kit abnormalities mainly occur around the LED lens fixed point.
2. Sliced analysis
2.1 Observation of the Gold Phase
Poor sample NG1, NG2 cross-section: drum coating layeration occurs between the aluminum substrate and the insulation layer.
Normal sample OK1 cross-section: The combination between the insulation layer and the aluminum substrate is not obvious abnormal.
2.2 SEM+EDS analysis
NG1 cross-section analysis shows that the drum package layer occurs between the anodizing layer of the aluminum substrate and the insulation layer, the separation interface does not see the presence of foreign matter, and the NG2 failure phenomenon is consistent with NG1.
OK1 cross-section analysis shows: The substrate structure is aluminum substrate + aluminum substrate anodizing layer + insulation layer + copper layer + white oil layer; the interface structure of each layer is good, no obvious abnormality.
3. Strip analysis
1) After the NG drum package is stripped, the peeling sides of the shedding interface is complete, and there is almost no residue of the insulation layer on the side of the aluminum substrate, indicating that the insulation layer is abnormally combined with the aluminum substrate. After EDS analysis, the aluminum substrate side interface contains Al, O, C, S elements, insulating layer side interface contains C, Al, O elements, did not find the existence of abnormal elements, preliminary exclusion of interface pollution on the impact of layering.
2) OK1 normal position stripped of the insulation layer after the aluminum substrate interface residue a large number of insulation layer material, indicating that the insulation layer and aluminum substrate combination is good; after EDS analysis, the aluminum substrate side interface contains Al, O, C, S elements.
4. Infrared spectroscopy
The insulation components of other batches & bad products NG batches are all bisphenol A-type epoxy resins, and the degree of curing is high, and there is no obvious difference in the curing degree between the two batches.
5. Thermal stress testing
Unbaked sample: After three tradonic tests the bad NG batch PCB appeared abnormal drum kit, the phenomenon is consistent with the bad failure, the slice shows that the drum coating stratification occurs between the insulation layer and the aluminum substrate; while the bad product other batches do not see the drum package and other obvious abnormalities, the slicing shows that the combination between the insulation layer and the aluminum substrate is not abnormal.
After baking After three tradication tests the bad NG batch and other batches of bad products have not seen obvious abnormalities such as drum packs, and the slicing shows that there is no abnormality between the combination between the insulation layer and the aluminum substrate.
In summary, the cause of abnormal drum packs in the NG batch of optical board bad products is directly related to PCB moisture.
6. Discussion and analysis
The factors that usually affect the strength of the interface between the insulation layer and the aluminum substrate are as follows:
1 There is pollution in the layered interface;
2 PCB moisture;
The insulation layer is not completely cured.
Through stripping analysis, the layered interface does not find the existence of abnormal elements, so the exclusion of the interface is contaminated; thermal stress analysis results, prove that the PCB drum package is directly related to the plate moisture; infrared spectral analysis results, indicating that the insulation layer solidifies well; so the cause of abnormal drum kit abnormality of bad products is directly related to the PCB moisture.
The reason for the difficulty of coating the bulge after the PCB moisture is speculated that after the PCB is dampened, the insulation layer absorbs the expansion of water vapor, weakens the interface binding state between the insulation layer and the aluminum substrate, and when the internal stress is repaired at high temperature, eventually leads to the interface detachment and the drum package layering is abnormal.
In summary, the reason for the abnormal local drum package in the aluminum substrate repair process is directly related to the PCB moisture.
Recommendation: Pre-baked before re-opening.