《In the previous article》In , we have established a knowledge framework for the properties and applications of metal materials and sorted out the core steps of scientific material selection. However, the theory needs to be tested in practice.
This article will focus on the actual combat link: how to use advanced detection technology to provide reliable data support for material selection decisions? How to balance performance and cost in a project? And through real cases, the consequences and solutions of improper material selection are revealed.
Is the performance standard? Key Indicators and Testing Technologies
Composition
analysis: Through spectroscopy and chemical analysis, determine whether
the content of various elements in the material meets the requirements
of the grade composition limit. 2,
mechanical properties: including tensile strength, hardness, toughness,
ductility, etc., through tensile testing, impact test evaluation. 3,
electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity: directly affect the heat
dissipation design, such as mobile phone shell need to take into
account the thermal and electromagnetic shielding. Chemical
stability: through salt spray test, acid and alkali soaking simulation
of the actual use environment (such as insulation cups need to be
resistant to water, tea, coffee corrosion). Fatigue
performance: Evaluate the life of the material under the cycle stress
and the key performance indicators of long-term safe service (such as
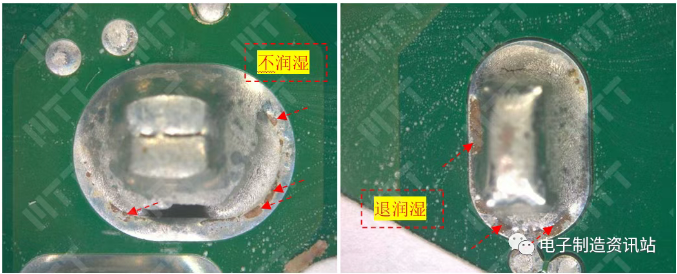
car chassis parts). Microstructure: The metallographic microscope observes the size and distribution of grain and determines the process defects.
Ingredient analysis instruments & testing technology introduction
Laboratory commonly used metal material detection methods and their applicable scenarios:
Technical comparison: OES and XRF are suitable for rapid field inspection, but XRF has superior non-destructive properties; ICP-OES/MS has higher precision, but requires complex pre-processing, and is suitable for laboratory precision analysis.
How to balance performance and cost?
Taking the thermos cup as an example, the selection of materials needs to be considered comprehensively: Safety: Food grade stainless steel (such as 316) needs to meet the GB 9684 standard austenitic stainless steel. Corrosion
resistance: 316 stainless steel can withstand acidic beverages (such as
lemon juice) for a long time because of molybdenum. Thermal
conductivity: The double-layer vacuum structure can reduce thermal
conductivity, but the thermal conductivity of the material itself needs
to be moderate. Cost: 304 stainless steel cost-effective, 316 is suitable for high-end demand.
How to balance performance and cost?
A
smart watch shell: use titanium alloy (lightweight + sweat corrosion
resistance), through XRF to verify the uniformity of the coating. New
energy vehicle battery housing: the use of aluminum alloy (lightweight +
excellent heat dissipation), through the salt spray test to ensure
environmental corrosion resistance. In
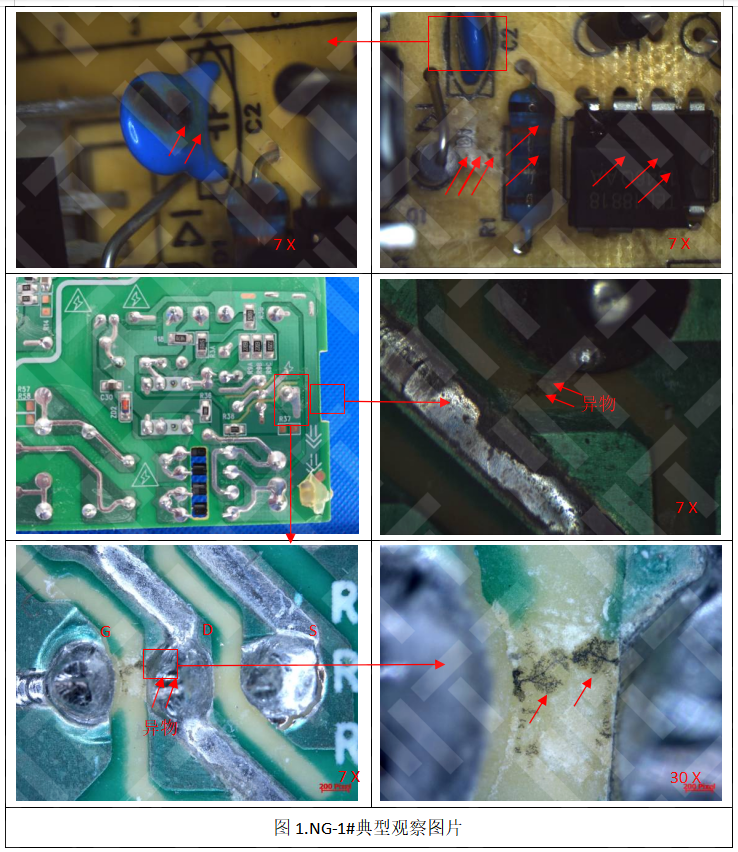
coastal equipment, 304 bolts are stress-corrosive cracking, and there
is no Mo (PREN=19) in 304, which cannot resist chloride ion erosion →
316 containing Mo (PREN=25). Copper
connector plug force attenuation, phosphorus bronze contact after high
temperature and high humidity elasticity decline; through component
analysis found that the Sn content is insufficient (<5%),
insufficient aging, and then recommended to increase Sn to 6-8% (such as
C5191). Aluminum
alloy shell intergranular corrosion, the product in the anodized after
the corrosion pattern; detection component analysis Fe impurity
exceeding the standard (>0.5%) to form the Al3Fe cathode phase,
accelerate local corrosion → control Fe <0.2%. The
selection of metal materials is a subtle art that combines material
science, testing technology and engineering experience. From accurate
component analysis to rigorous performance verification, rigorous data
support is required at every step.
Everyone, here’s a good gift waiting for you! “Down with a little trick.” Under the premise of ensuring core functions, the most effective metal material you have used is the "cost reduction" method. F. Other methods 在Share your usual tricks in (select letters) And tell the reason. We will be in the comments section on July 28th. Choose three fans. Give the following gift (one choice) 1! Failure analysis case book Household tool kit
A. Search for domestic alternatives (performance standards)
B. Optimized design to reduce material usage
C. Choose a lower-cost alloy grade (such as 6 series aluminum instead of 7 series)
D. Improved process to reduce scrap rates
E. There is no particularly good way for the time being.