In today's popularization of smart phones, mobile phone reliability has become the focus of user attention. A high-reliability mobile phone can not only bring a smooth experience, but also do not fall off the chain at a critical moment. So, what factors affect the reliability of mobile phones? How to upgrade? Today, let’s take a closer look at it.
History of mobile phone development From simulation to intelligent leap The development of mobile phones can be said to be the evolution of a communication technology. From the big brother of to
the 5G mobile phone that now integrates ultra-high-speed transmission,
ultra-low latency, and large-scale connectivity, every technological
innovation has brought about a huge change in mobile phones. Big Brother
can only carry out voice business, and in the 2G era, mobile phones began to support SMS, MMS, and even can handle mail and web pages. In the 3G era, the combination of mobile phones and the Internet is more closely, and multimedia forms have begun to enrich. In the 4G era, the network connection is faster and more stable, and the rise of APP has made mobile phone functions more diverse. In the 5G era,
the deep integration of artificial intelligence technology with mobile
phone hardware and software has made mobile phones have unprecedented
intelligence, convenience and personalization capabilities.
Cell Phone Structure and Function Precision and Diversity Integration A mobile phone, seemingly simple, but the internal structure is complex.
From motherboards to batteries, from displays to cameras, every
component is carefully designed and manufactured. The function of the
mobile phone covers many aspects such as calling, surfing the Internet,
taking photos, and entertainment. Today, with the continuous advancement
of technology, the functions of mobile phones are still expanding, such
as health monitoring, mobile payment, etc., to make our lives more
convenient.
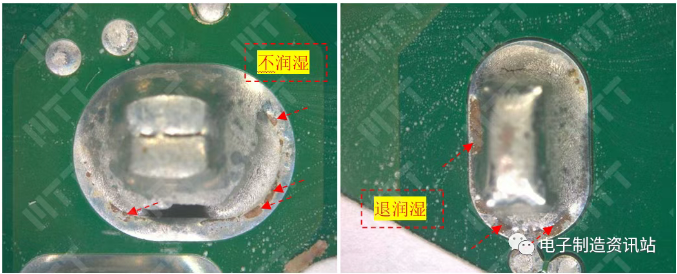
Mobile phone reliability test project Rigorous and comprehensive testing The
reliability of mobile phones is affected by a variety of factors, which
are carried out throughout the entire process of mobile phone research
and development, production and use. From the research and development stage, design defects are
one of the important factors affecting the reliability of mobile
phones. For example, the heat dissipation design is unreasonable, which
will cause the mobile phone to run for a long time or be in a high
temperature environment, and the heat cannot be dissipated in time,
resulting in a decline in the performance of the mobile phone, and even a
crash, restart and other issues. The structural design is not
reasonable, which may affect the assembly accuracy of the mobile phone
and the stability of the internal components, and increase the risk of
failure of the mobile phone. In the production process, hardware quality is the key.
The chip, as the "brain" of the mobile phone, the quality directly
determines the speed and stability of the mobile phone. If a low-quality
chip is used, it may cause the mobile phone to run stutter and crash
frequently. In addition, the quality of electronic components such as
capacitors, resistance, etc. can not be ignored, and the instability or
poor quality of their parameters may affect the normal work of the
circuit, which in turn leads to the failure of the mobile phone.
The use of the environment also
has an important impact on the reliability of mobile phones. In terms
of temperature, in a high temperature environment, the performance of
the mobile phone battery will decrease, the battery life will be
shortened, and the performance of electronic components may also be
affected, accelerating aging; in a low temperature environment, the
discharge capacity of the battery will be reduced, which may lead to the
automatic shutdown of the mobile phone. In terms of humidity, the high
humidity environment will make electronic components damp, causing short
circuits and other problems; low humidity environment may produce
static electricity, causing damage to mobile phones. In addition, dust
and vibration is also a factor that can not be ignored, dust into the
inside of the mobile phone may affect the heat dissipation and the
normal work of the circuit, and vibration may lead to loose and fall off
internal components of the mobile phone, causing poor contact.
What are mobile phone reliability improvement strategies? In
response to the above factors that affect the reliability of mobile
phones, we can adopt the following strategies to improve the reliability
of mobile phones. 在In the research and development stage,
we should pay attention to optimizing the design. Strengthen the heat
dissipation design, the use of efficient heat dissipation materials and
heat dissipation structure, such as heat sinks, heat pipes, etc., to
ensure that the mobile phone can maintain good heat dissipation
performance in various environments. At the same time, improve the
structural design, improve the assembly accuracy of the mobile phone and
the stability of internal components, and facilitate subsequent
maintenance and upgrading. In the production process,
the quality of the hardware should be strictly controlled. Choose
high-quality chip and electronic components suppliers to conduct
rigorous inspection and testing of raw materials to ensure that they
meet high standards. In the production process, increase multiple
inspection processes, and conduct comprehensive performance testing and
reliability testing of semi-finished products and finished products,
such as high temperature testing, low temperature testing, vibration
testing, etc., to detect and solve potential quality problems in a
timely manner. In the process of use, users should also pay attention to some things to protect the mobile phone
Avoid exposing your phone to high or low temperatures for a long time,
such as not placing your phone in a car that is directly sunny or
outside the cold. At the same time, pay attention to keep the phone dry,
to avoid the use of mobile phones in a humid environment. In addition,
regularly clean the dust inside the phone to avoid dust accumulation
affecting heat dissipation and normal operation of the circuit.
Witness the power of mobile phone reliability High and low temperature + soft pressure test after the display leakage
Mobile
phone reliability is a comprehensive concept, affected by a variety of
factors. By optimizing the design, strictly controlling the quality of
the hardware and the correct protection of the user during use, we can
effectively improve the reliability of the mobile phone and bring users a
more stable and smooth experience.
Note: The above picture is partly derived from external channels, and is only for learning communication and reference use.