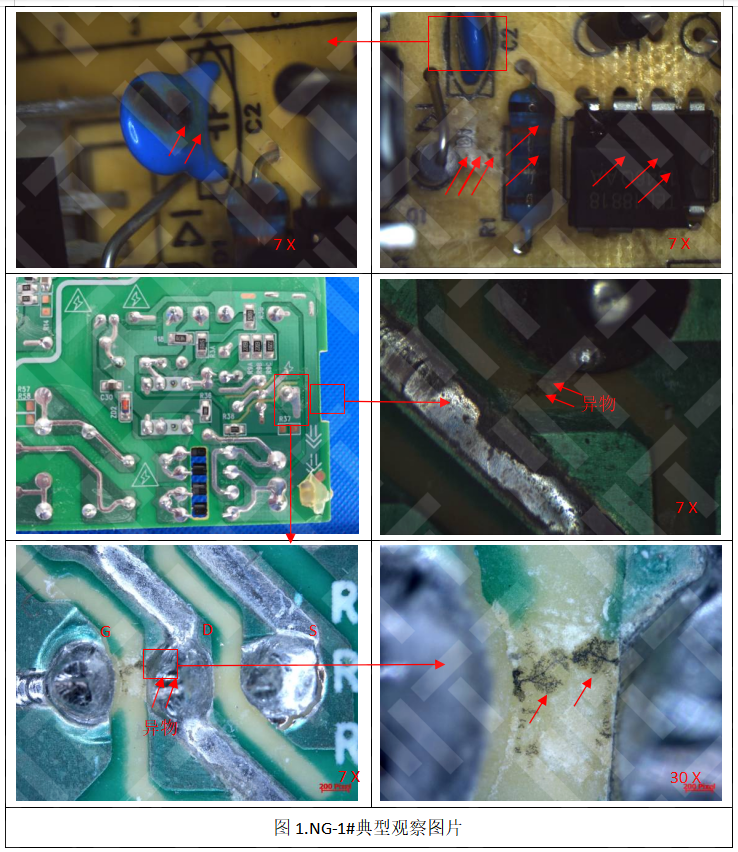
In
the field of precision manufacturing, even if it is a seemingly
insignificant assembly cracking problem, every minor defect may become a
major hidden danger of product quality and safety, resulting in tens of
millions of losses. We
found that a stamped copper strip after stamping, in the assembly
process found that there are terminals cracking, cracking has occasional
irregularity. This seemingly ordinary failure is behind the potential
major hidden dangers in the rolling process. This
article will take you to analyze this case in depth, starting from the
cracking phenomenon of the spouse, gradually uncovering the truth about
the surface layering defects of the material, and exploring the reasons
behind it. 1. Low observation. It
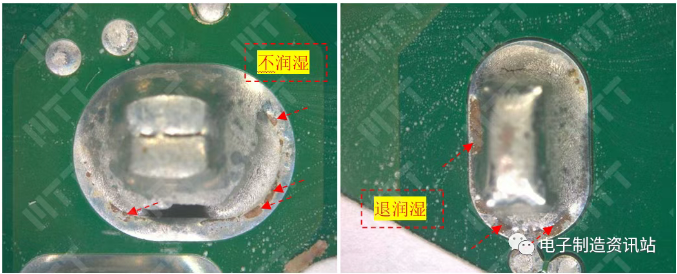
can be seen from the figure that the specimen NG crack is located in
the bending part of the terminal, near the center of the curved arc,
close to the front of the terminal, and the bending part of the crevice
is the most severe position in the bend. The crack has a certain width
and depth, and the crack edges are visible layered gap distribution. 2. Surface analysis The
two edges of the crack have overlapping characteristics, and the
granular tin plateding distribution is visible in the layered gap of the
crack, which indicates that the cracks have existed before the tin
plating. The silhouette of the edge of the crack coincides, indicating
that the crack position is intact before bending, that is, the crack is
caused by bending when punching. Spectroscopic analysis shows that the
local surface Zn content of the coating is high. 3. Metamorphic analysis It
can be seen from the figure that no obvious layering and other defects
have been found at the bending, cracks can be seen at the bending, the
cracks are trapezoidal, and there is no cracking extension at the bottom
of the trap. Before plating Sn, the cracks already existed. The other
crevice can see the "W"-shaped sharp angle, and the "W" sharp angle can
be seen with the overlap contour of the gap, indicating that after the
sharp angle of the crack here is stretched, the original layered gap is
open. Figure
5 shows the gold phase diagram after the corrosion of the specimen. It
can be seen from the figure that the matrix metal phase can be seen in
the distribution of twin crystals, the grain is fine, and the grain
uniformity is better. In the bending deformation area, it can be seen
that the grain is elongated, and the sharp angle area is close to the
outer surface tissue, the core area of the substrate core and the grain
in the uncurved area is still in an equal axis, that is, no more obvious
deformation occurs. 4. Ingredient Analysis & Hardness Analysis Table
1 shows that the chemical composition of the material meets the
requirements of the C2600 grade chemical composition in JIS H3100-2018,
and the cross-section hardness distribution is more uniform.
5. Bending analysis Take
OK samples along the bending process, low observation, as shown in
Figure 6. It can be seen from the figure that the tin-plated layer of
the bending and tensile surface is cracked, and the brass substrate is
exposed. In order to observe whether the substrate is cracked, a
metallographic analysis of the specimen is required. The
metallographic analysis of the bend sample will be bent, as shown in
Figure 6. It can be seen from the figure that the tensile surface matrix
of the bending part does not see the crack, and the compression surface
can be seen to extend the thickness of the belt along the belt, and it
can be seen that the tensile surface has a good extension performance
under a certain bending and curvature when bending the curvature. 6. Discussion and Summary The
study believes that in the plastic deformation stage, copper and copper
alloy grains will be slipping and forming steps, grain orientation,
size is different, the degree of distortion is different, will form
different surface conditions, such as smooth, wrinkles and cracks. It
can be seen from the outline of the edge of the crack, the crack can be
partially coincident, that is, the crack belongs to the external force
to be separated. The metallographic phase can be seen, compared with the
significant plastic deformation of the grain on the surface of the
trapezoidal crack subsurface, the grain of the tissue of the sharp angle
of the trapezoidal crack near the outer surface of the tension is not
significantly elongated, that is, no more obvious plastic deformation
occurs. After the crack subsurface is opened, the crack does not extend
further in the direction of thickness and the bending test can prove
that the material has excellent anti-stretching plastic deformation
ability. The bending structure of the NG specimen has a layering defect,
which is located in the subsurface layer, and the layering is first
broken during the bending process. To
sum up, it can be seen that the defect here is the deep pressure on the
surface of the strip, because the material has excellent plasticity,
the subsequent rolling deformation, the tape extends at the crushing
site, forming a layered defect. Comprehensive analysis can be seen, the material subsurface has a layered defect, is the main reason for the cracks in the bending when the punching.