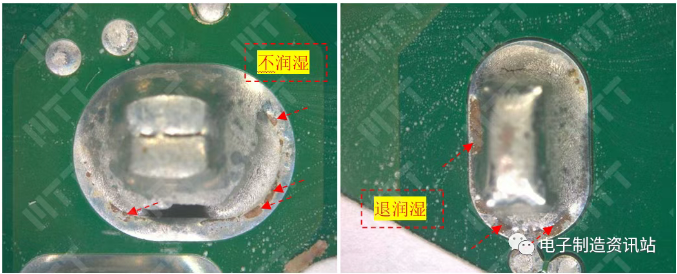
In material failure analysis, fracture is often a complex process, and finding the "starting point" of fracture - the fracture source area, just as the detective locks the first scene when solving the case. It not only reveals the initial trigger for fracture, but also provides important clues for preventing similar accidents and optimizing product design.
1:The fracturing source zone: Why is the “starting point” of fracture so important? The
break does not happen overnight, but begins to expand gradually from a
weak point. The cleft source area is usually the result of a combination
of internal defects, external stress concentration, or environmental
factors. Accurately locate the source of the separation, can help
engineers: 1, the source of retroactive failure: determine whether it is a material problem, process defects or a fracture caused by improper use; 2, improve product design: optimize the structure or material selection for weak links; 3、3, to prevent the recurrence of accidents: through targeted measures to avoid the recurrence of the same kind of fracture. 2:"Talk": the typical breakage of the cleft source judgment According
to the characteristic pattern of the break of the polymer material, we
can find the location of the cracking source like the interpretation of
the password: glyph The
human character on the break, the direction of its "head" directly
points to the crack source. This phenomenon stems from the direction of
energy release during the crack expansion process. parabolic The
vertex of the parabola is the location of the starting source. This
type of pattern is often broken when the material is hit by the load. Direction of the river The small cracks of the line converge into a "river", and its flow direction points to a larger step or defect. Point extension With
the starting source as the center, the cracks expand outward in a
radial form, similar to the "sun light", and the central point is the
source. In
addition, share some of the bubbles or traces of chemical reagent
erosion in some of the broken junctions we have encountered before, and
see what differences exist with the above-mentioned cracking source
break characteristics. Undrying Chemical reagent soak crack road 1 Chemical reagent soak cracked road two
The
meaning of the source judgment is not only to "find the problem", but
also to "solve the problem". It is not only a bridge between failure and
engineering practice, but also one of the core capabilities of material
engineers.
Note: The above picture is partly derived from external channels, and is only for learning communication and reference use.
Interactive benefits Analyze the crack source pattern in the picture and explain the basis for judgment. The answer was published on May 23, 2025. Send out 3 fans. Customize the charging mouse pad or failure analysis case book! (Quickly forward the praise, one step closer to the grand prize!)